When does overtime occur, in what situations is it permissible and how to settle it? You can find all the information about overtime in our article.
1. Overtime – when does it occur?
Overtime is work performed over:
- the employee's daily working time norm,
- extended daily working time, resulting from the employee's system and working time schedule
- the applicable weekly standard of working time
An order to work overtime can be given in any way, including implicitly. Thus, the supervisor's lack of objection to the employee's performance of professional duties in the presence of the supervisor during hours exceeding his or her daily working time may be classified as an order to work overtime.
An employee is obliged to carry out an order to work overtime if the order to work overtime has been issued in accordance with the law and does not violate the rules of social coexistence and is not contrary to the employment contract.
2. Overtime – admissibility and limits
Overtime is allowed for:
- the necessity to carry out a rescue operation in order to protect life or health, to protect property or the environment, and the need to remove failures (flood, fire, construction accidents, failures of machinery and equipment).
- the employer's special needs, which may result, for example, from the need to perform the order urgently, on time or due to employees' sickness absence.
However, in the company's internal regulations (work regulations, collective agreement) or in the employment contract, the employer may set a different, higher limit of overtime, but it may not exceed 416 hours in a calendar year.
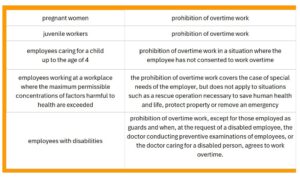
Not all employees can be ordered to work overtime by their employer. These include:
3. Overtime for part time employees
Part-time employees are subject to the same daily and weekly work standards as full-time employees.
In the case of work exceeding the working hours specified in the contract, but within the limits of the applicable standards, we are dealing with overtime work, it is not overtime work.
Overtime starts only when the working time standards are exceeded, i.e. 8 hours a day or an average of 40 hours a week in basic working time.
Example:
A 1/2-time employee works from Monday to Friday from 08:00 to 12:00. Work from 12 to 4 p.m. will be an additional work time, and any hour worked after 4 p.m. will be overtime.
4. Overtime – compensation in the form of remuneration
One of the ways to settle overtime work is a cash equivalent, which includes:
- normal remuneration, including basic salary and fixed allowances (e.g. function-related allowance, seniority allowance, fixed bonuses)
- overtime allowance in the amount of:
- 100% of remuneration for overtime attributable to:
- at night – on Sundays and holidays that are not working days for the employee, in accordance with the applicable working time schedule,
- on a non-working day granted to an employee in exchange for work on a Sunday or a holiday
- 50% of remuneration for overtime work falling on any day other than the one described above
- 100% of the remuneration for each hour of overtime work due to exceeding the average weekly standard of working time in the adopted settlement period.
5. Overtime with lump sum billing
In the case of employees who work outside the workplace on a permanent basis, the remuneration may be replaced by a lump sum, the amount of which should correspond to the expected number of overtime hours.
The lump sum may be reduced proportionately in the event of non-work, for example due to illness. On the other hand, working fewer hours than assumed is not the basis for reducing the lump sum amount.
When determining the amount of the lump sum for overtime, it should be remembered that it cannot exceed 8 hours per week, as this would mean exceeding the weekly working time in the adopted settlement period.
6. Overtime – Compensation for Time Off
Another way to compensate for overtime work is to grant time off. This can be done at the employee's request or without the employee's request.

With this form of compensation, the employee receives remuneration for time off, but without an allowance.
Overtime work compensated by time off counts towards the annual overtime limit.
7. Overtime – working on a day off
An employee who worked on a non-working day resulting from the working time schedule in a 5-day work week is entitled to another non-working day granted to him or her until the end of the settlement period, on a date agreed with the employee.
Example:
An employee who worked from Monday to Friday was told to work 2 hours on Saturday. In exchange for this work, he is entitled to a full day off.
Failure to grant a day off in exchange for work on the day off referred to above is an offence against the employee's rights punishable by a fine of PLN 1,000 to PLN 30,000.
8. Overtime for executives
Employees who manage a workplace on behalf of the employer and managers of separate organisational units do not receive remuneration and an allowance for overtime work.
The right to remuneration and an allowance in the amount of 100% is granted to managers working overtime on Sundays and holidays if they have not received a day off in exchange for working on such a day.
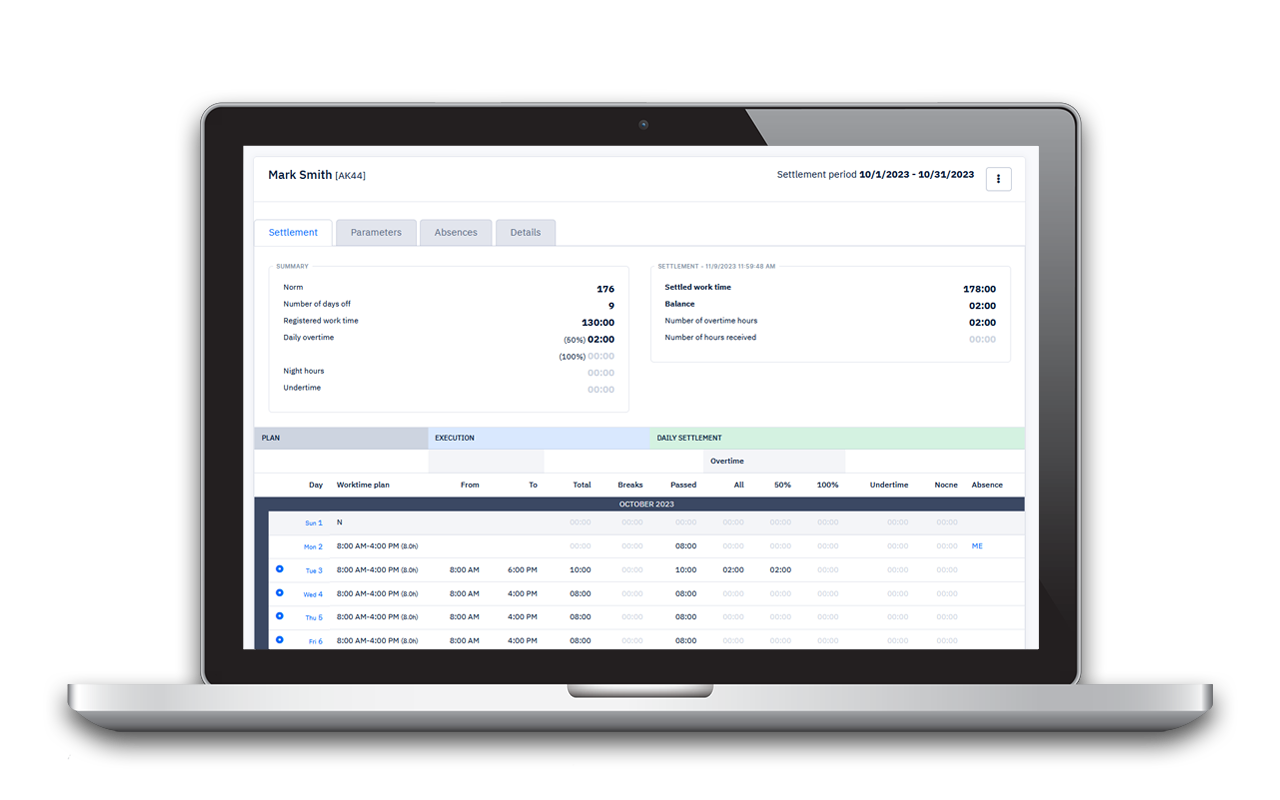
Overtime calculation in Time Harmony
Time Harmony – a system for electronic registration, planning and settlement of working time is a convenient tool for settling overtime. The system calculates overtime with +50% and +100% addition, as well as allows to settle overtime with time off.
Easily manage your company's working time

