Parental leave is one of the most important employee rights, supporting parents in childcare and balancing family and professional duties. The Labor Code strictly regulates the conditions, duration, and protection for employees. In this article, we explain how parental leave labor code works, what rights employees have, and how companies can manage leave effectively with the support of Time Harmony.
What is Parental Leave Under the Labor Code?
Legal Basis for Parental Leave (Articles 182¹a–182¹g)
Parental leave is governed by Articles 182¹a–182¹g of the Polish Labor Code. It follows maternity leave (or leave under the conditions of maternity leave). Both mothers and fathers are entitled to it, and the law allows for flexible division of parental leave between parents.
Who Can Apply for Parental Leave?
Parental leave is available to employees under an employment contract. Parents may use it individually, share it, or even take parts of the leave simultaneously.
Duration of Parental Leave in the Labor Code
Leave for One Child
According to Article 182¹a, if one child is born, parents are entitled to 41 weeks of parental leave.
Leave for Multiple Births
If two or more children are born, parents are entitled to 43 weeks of parental leave.
Additionally, part of the leave can be used until the end of the calendar year in which the child turns six.
Rules for Using Parental Leave
Division of Leave Between Parents
Parental leave may be divided into a maximum of five parts, with each part lasting at least eight weeks (with certain exceptions). Parents can take leave consecutively or at the same time.
Application Deadlines and Form
According to Article 182¹c, the application for parental leave must be submitted in writing at least 21 days before the planned start of the leave.
Salary During Parental Leave
Maternity Benefit During Parental Leave
During parental leave, employees do not receive their salary but instead receive a maternity allowance paid by the Social Insurance Institution (ZUS).
Amount of the Allowance
If the application covers the full maternity and parental leave immediately after childbirth, the allowance is 81.5% of the calculation base for the entire period. Otherwise, it is 100% for the first six weeks (for one child) and 60% for the remaining weeks.
Parental Leave and Employee Rights
Protection Against Termination
According to Article 177 of the Labor Code, employees are protected during parental leave. The employer cannot terminate or dissolve the employment contract during this period.
Return to Work After Leave
After parental leave, employees have the right to return to their original position or, if unavailable, to an equivalent one with the same pay.
Managing Parental Leave With Time Harmony
Managing long-term parental leave requires proper workforce planning. Time Harmony helps HR departments and managers by automating leave requests, tracking schedules, and analyzing the impact of absences on business processes. This allows companies to plan replacements, reduce downtime, and maintain operational continuity.
Conclusion – Parental Leave Labor Code in Practice
Parental leave, regulated by the Labor Code (Articles 182¹a–182¹g), provides parents with flexible childcare options and protects their employment. For employers, managing parental leave effectively is equally important, and digital tools like Time Harmony make the process efficient.
The parental leave labor code is not only a legal obligation but also a valuable element of employee satisfaction and long-term workforce loyalty.
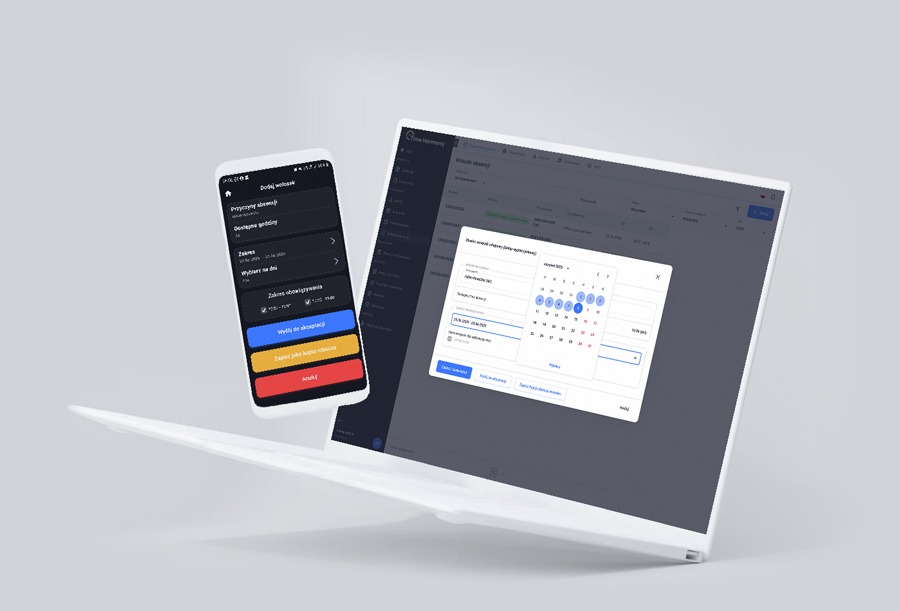
Easily manage your company's working time

